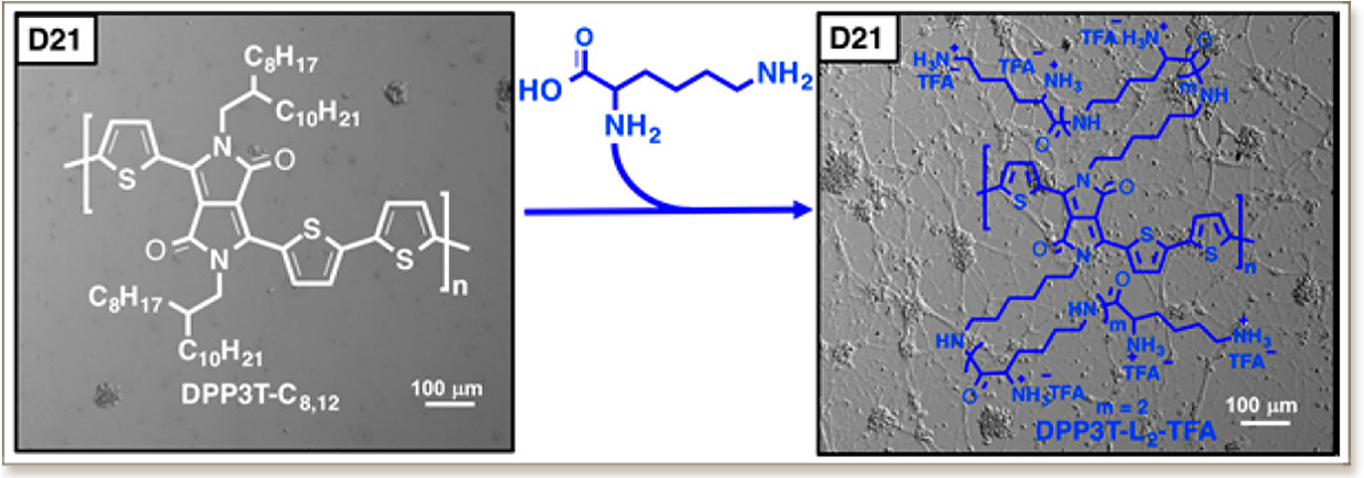
Organic semiconductors are being increasingly used for a variety of biological applications, such as biochemical sensors, drug delivery, and neural interfaces. However, the poor adhesion of cells to the typically hydrophobic, neutrally charged, and low-surface energy semiconducting thin films limits their use as part of in vitro, cell-integrated bioelectronic devices. In this work, we investigate the influence of lysine side chain units incorporated in a diketopyrrolopyrrole semiconducting polymer on neural cell adhesion and growth and evaluate their function in electrical devices. Synthesis of such biofunctionalized polymers obviates the need for biological coating steps while changing the surface physiochemistry, which makes them promising for applications in bioelectronics.